image:
view more
Credit: Cyborg and Bionic Systems
At
present, stroke has become one of the most serious neurological
diseases, which is usually accompanied by movement disorders and
cognitive impairment. In recent years, the number of stroke patients has
increased annually . Most stroke patients are accompanied by movement
disorders, which seriously affect the normal life of patients. A
groundbreaking study conducted by Shihao Sun and colleagues, recently
published in the Cyborg Bionic Systems journal, has introduced
innovative findings in the realm of Functional Electrical Stimulation
(FES), particularly its application in muscle recovery and fatigue
management.
Functional electrical stimulation (FES)
technology is a new type of treatment, which is through the simulation
of the nerve on the muscle issued by the electrical signals for
rehabilitation training.
Functional Electrical Stimulation has been
a beacon of hope for patients suffering from severe neurological
disorders such as stroke, which often leaves individuals with
significant movement and cognitive impairments. This new research
primarily focuses on optimizing the parameters of FES to enhance muscle
recovery without causing additional muscle fatigue, a common setback in
previous applications.
The study meticulously analyzed the
effects of FES parameter settings on muscle health, establishing a
crucial relationship between current amplitude and the optimal
stimulation time. This relationship is key to preventing muscles from
entering an excessive fatigue state, thereby promoting more effective
recovery.
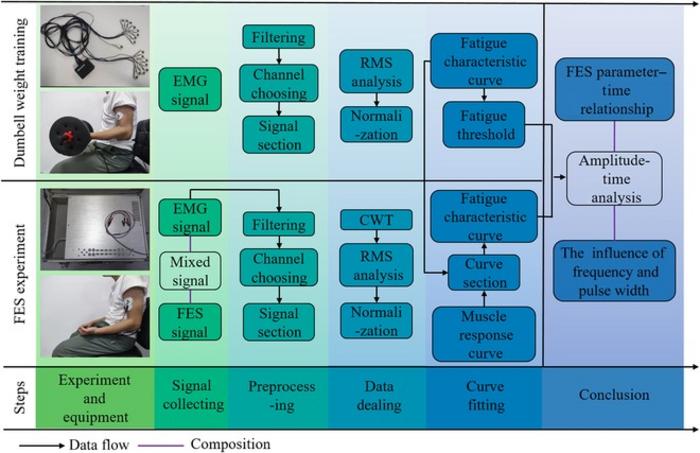
In a detailed experiment involving ten
subjects undergoing dumbbell weightlifting training, the research team,
led by Sun and Guizhi Xu from Hebei University of Technology, China,
monitored the subjects’ muscle responses via surface electromyography
(sEMG). This technique helped them craft a nuanced understanding of how
muscles react under different levels of electrical stimulation.
Their findings suggest that the most
significant parameter in FES is the current amplitude, which, when
optimized, can prevent muscles from over-fatigue.This breakthrough is
depicted in a linear curve developed during the study, demonstrating a
direct relationship between current amplitude and maximum safe
stimulation time. This curve is anticipated to be a valuable tool for
clinicians and therapists focusing on rehabilitation through FES.
Moreover, the research explored the
effects of varying the frequency and pulse width of the FES, uncovering
that these adjustments could significantly impact muscle fatigue rates
and recovery times. This has important implications for the
customization of FES treatments to individual patient needs, potentially
leading to more personalized and effective rehabilitation strategies.
By integrating a complex array of
biomedical engineering techniques, including wavelet transform and RMS
normalization, the team was able to provide robust scientific insights
that pave the way for the next generation of FES devices. These devices
could offer more adjustable and patient-specific settings, reducing the
risk of muscle damage and enhancing the overall effectiveness of
recovery therapies.
This study not only marks a significant
advancement in the use of Functional Electrical Stimulation for muscle
recovery but also highlights the potential for future technologies to be
more adaptable to the physiological conditions of different patients,
ensuring safer and more effective recovery processes.
As the research moves forward, further
studies will likely focus on refining these parameters and exploring
additional ways to harness the power of FES in medical rehabilitation.
The ultimate goal is to provide stroke survivors and individuals with
neurological impairments a more effective path to regain muscle function
and improve their quality of life.
The paper, “Function Electrical
Stimulation Effect on Muscle Fatigue Based on Fatigue Characteristic
Curves of Dumbbell Weightlifting Training” was published in the journal
Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Jun 6, 2024, at DOI: https://doi.org/10.34133/cbsystems.0124